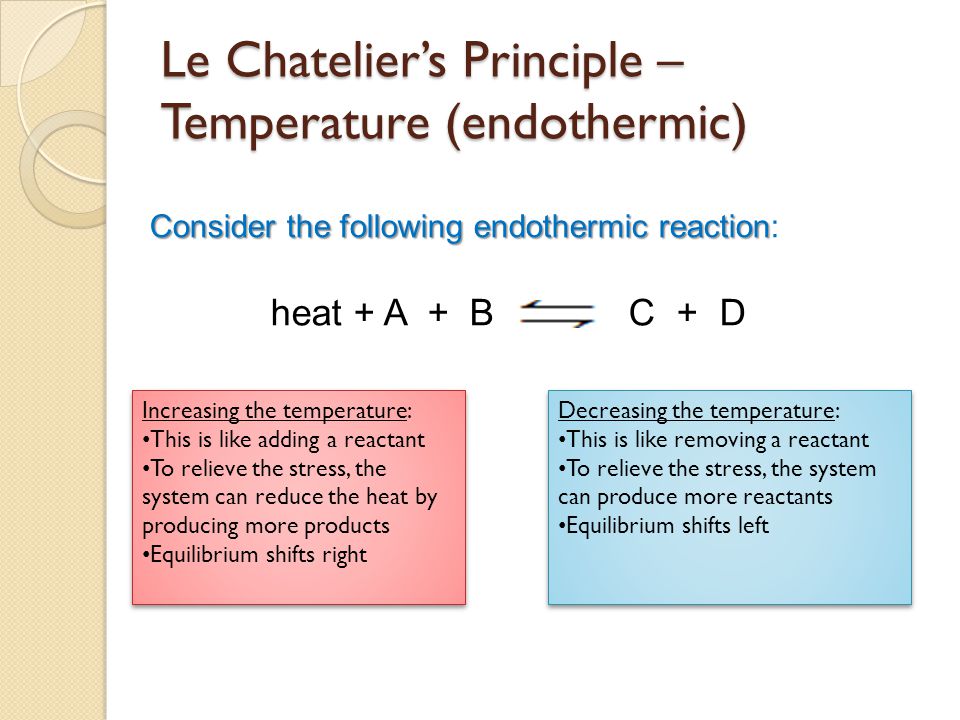
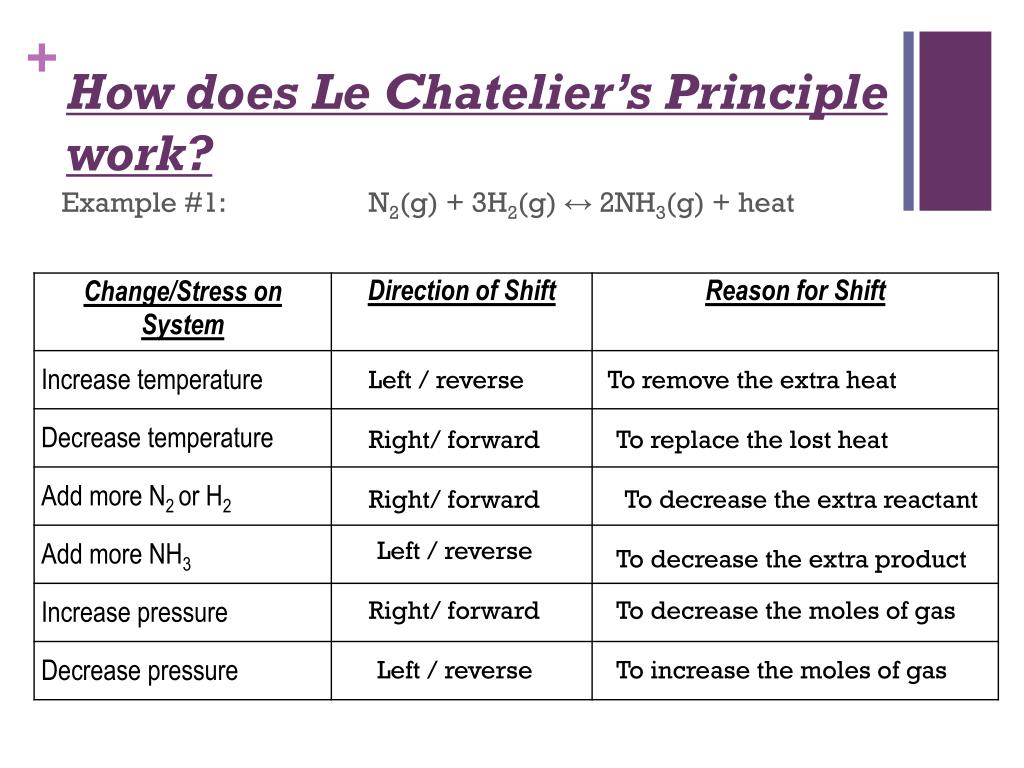
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium $$\ce{A>B}, \Delta H < 0 $$ Suppose I increase the temperature Now, quite a few people would invoke Le Châtelier's Principle and say that since "heat" is a product of this reaction, the equilibrium should shift backwardsOn the basis of Le Chatelier principle explain how temperature and pressure can be adjusted to increase the yield of ammonia in the following reaction N 2 (g) 3 H 2 (g) ⇋ 2 N H 3 (g) Δ H = − 9 2 3 8 k J m o l − 1 What will be the effect of addition of argon to the above reaction mixture at constant volume?Le Chatelier's Principle is important, because it allows us to shift an equilibrium to the side that we would like to favor For example the Haber Process produces ammonia reversibly #N_2(g) 3 H_2(g) > 2 NH_3(g)# The reaction is run at high pressures, because there are 2 moles of ammonia on the product side, but 4 moles of gas on the reactant side (3 mol of hydrogen and 1 mol of

7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Sl Youtube
Le chatelier's principle temperature decrease
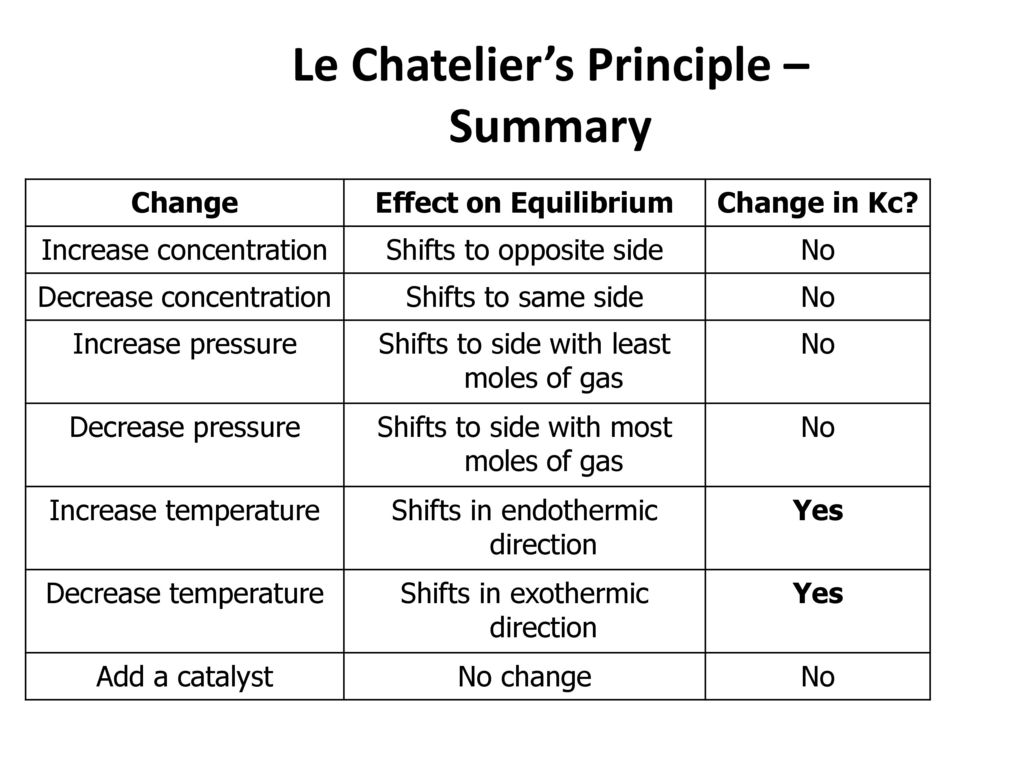
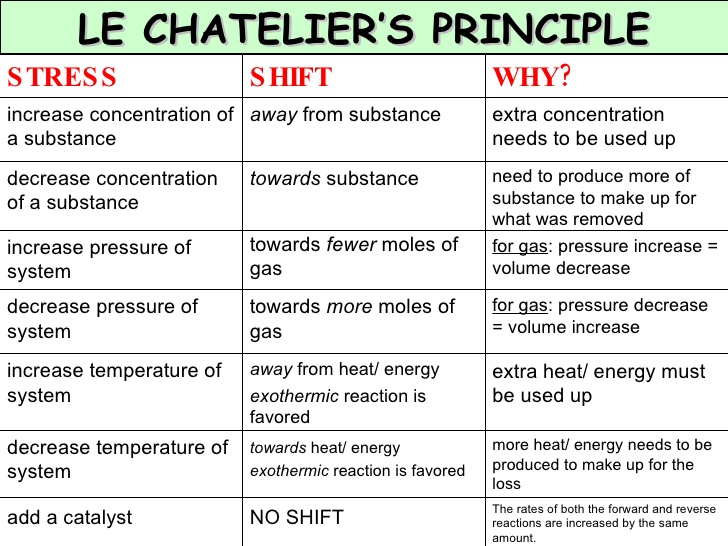
Le chatelier's principle temperature decrease-Sep 16, 14 · Le Chatelier's principle addresses how an equilibrium shifts when the conditions of an equilibrium are changed The direction of shift can be predicted for changes in concentrations, temperature, or pressure Catalysts do not affect the position of an equilibrium;Le Chatelier's principle when stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the reaction will shift in a direction that relieves the stress and a new equilibrium will be established n applied stresses changes in concentration, pressure, or temperature qstress caused by change in concentration p shift due to increase in concentration of a


Le Chatelier S Principle
Le Chatelier's Principle helps to predict what effect a change in temperature, concentration or pressure will have on the position of the equilibrium in a chemical reaction This is very important, particularly in industrial applications, where yields must be accurately predicted and maximised \Large Le Chatelier's PrincipleThis demonstrates Le Chatelier's principle the equilibrium shifts in the direction that consumes energy When heat is removed and the temperature decreases, the reaction shifts to the left and the flask turns colorless due to an increase in N 2 O 4 again, according to Le Chatelier's principleLe Chatelier's Principle on Change of Temperature As per the Van't Hoff equation, for an exothermic equilibrium, ∆H will be negative Increase of temperature shall decrease K 2 or decrease in temperature increases K 2 The opposite is true for an endothermic reaction
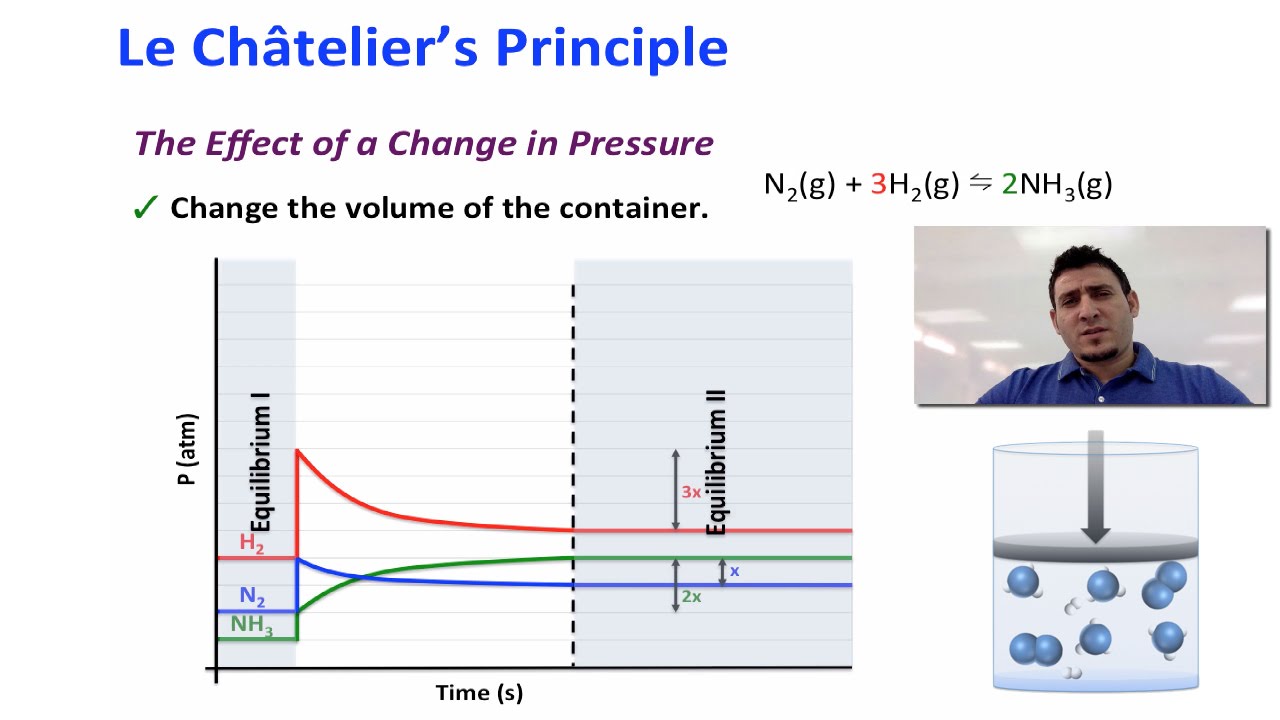
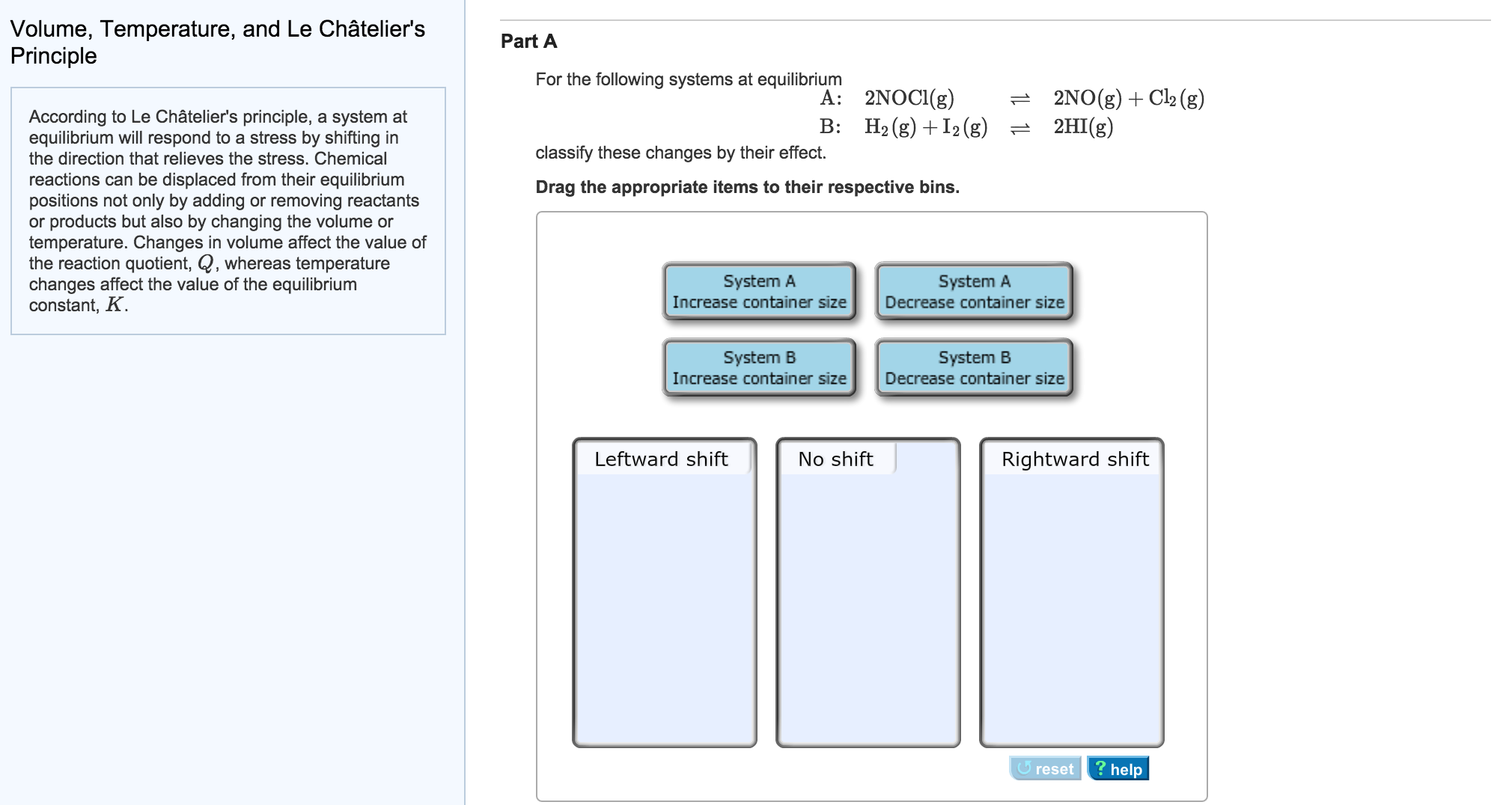
They help reactions achieve equilibrium fasterVolume, Temperature, and Le Châtelier's Principle Part A For the following systems at equilibrium A B 2NOCI(g) H2 (g) 2N0(g)Cl2(g) 2H1(g) 근 According to Le Châtelier's principle, a system at equilibrium will respond to a stress by shifting in the direction that relieves the stress, Chemical reactions can be displaced from their equilibrium positions not only by adding or removingLe Chatelier's principle The reactants, products, and energy associated with a chemical reaction According to Le Châtelier's Principle, an increase in the concentration of product will shift the chemical system to _____ left Le Châtelier's Principle states that when a change (pressure, temperature, concentration) is imposed on a
Nov 02, 19 · Le Chatelier′s Principle is the principle when a stress is applied to a chemical system at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift to relieve the stress In other words, it can be used to predict the direction of a chemical reaction in response to a change in conditions of temperature, concentration, volume, or pressureLe Châtelier's Principle Page 1 of 15 Properties of Systems in Equilibrium – Le Châtelier's Principle Objectives To perturb chemical reactions at equilibrium and observe how they respond Increase temperature of an exothermic reaction Shift to the left DecreaseAccording to Le Chatelier, the position of equilibrium will move in such a way as to counteract the change That means that the position of equilibrium will move so that the temperature is reduced again Suppose the system is in equilibrium at 300°C, and you increase the temperature to 500°C



Chemical Equilibrium The Concept Of Equilibrium No Chemical
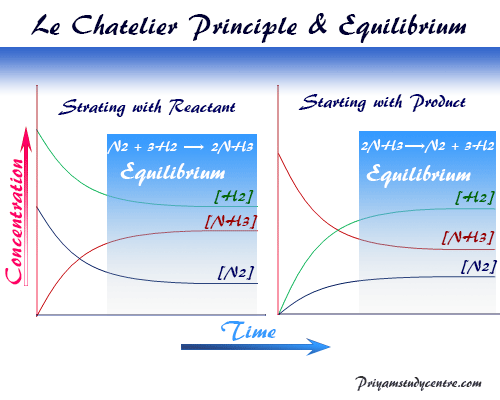


Le Chatelier Principle Definition Application Facts Priyamstudycentre
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsLowering the temperature in the HI system increases the equilibrium constant At the new equilibrium the concentration of HI has increased and the concentrations of H 2 and I 2 decreased Raising the temperature decreases the value of the equilibrium constant, from 675Decreasing the temperature will cause the system to shift left, shift right, stay the same to reach a new equilibrium 2SO 2 (g) O 2 (g) ⇄ 2SO 3 (g) Le Chatelier's principle is an observation about chemical equilibria of reactions



Chem 2 Chemical Equilibrium X Le Chatelier S Principle And Tempera
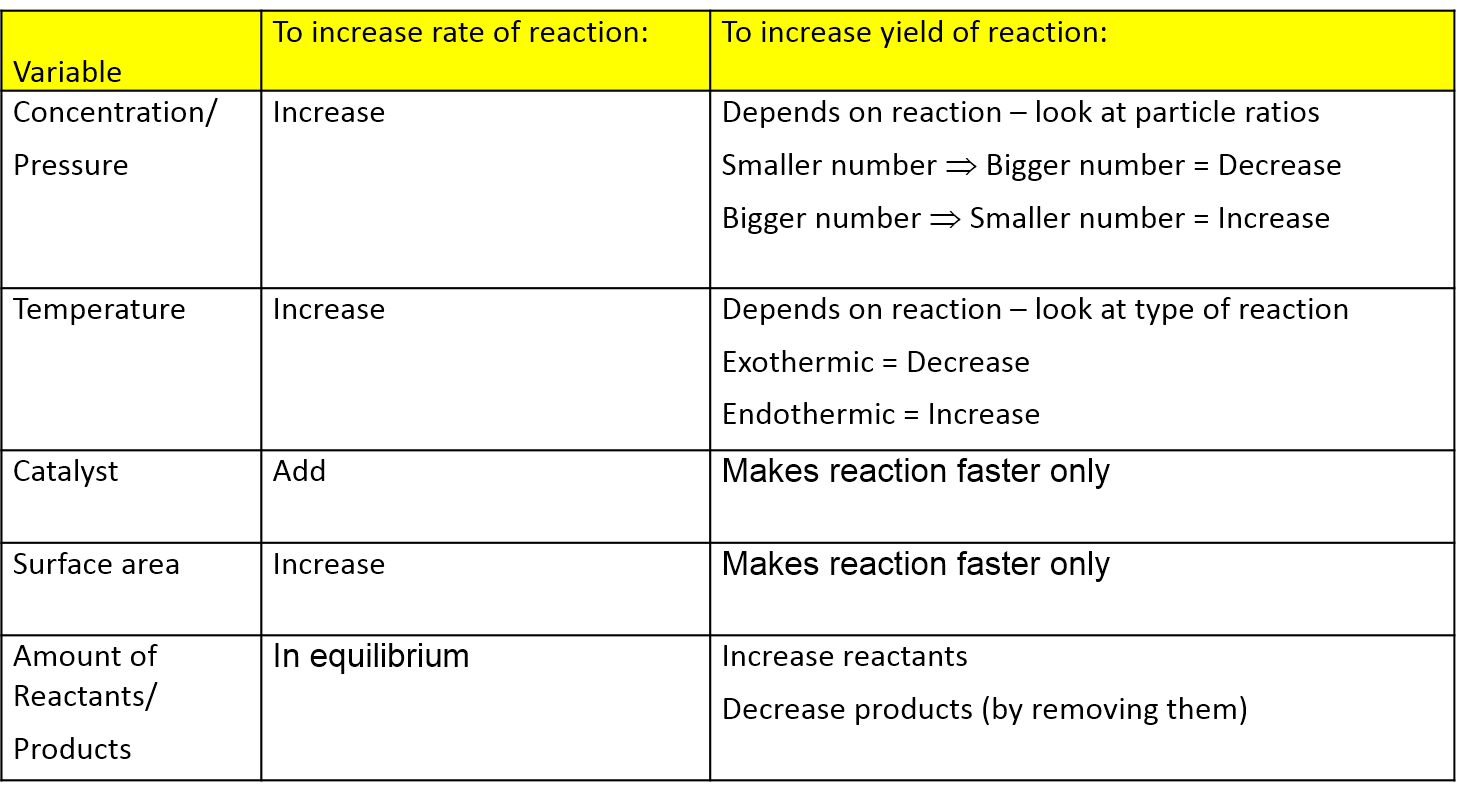


Le Chatelier S Principle Vce Chemistry
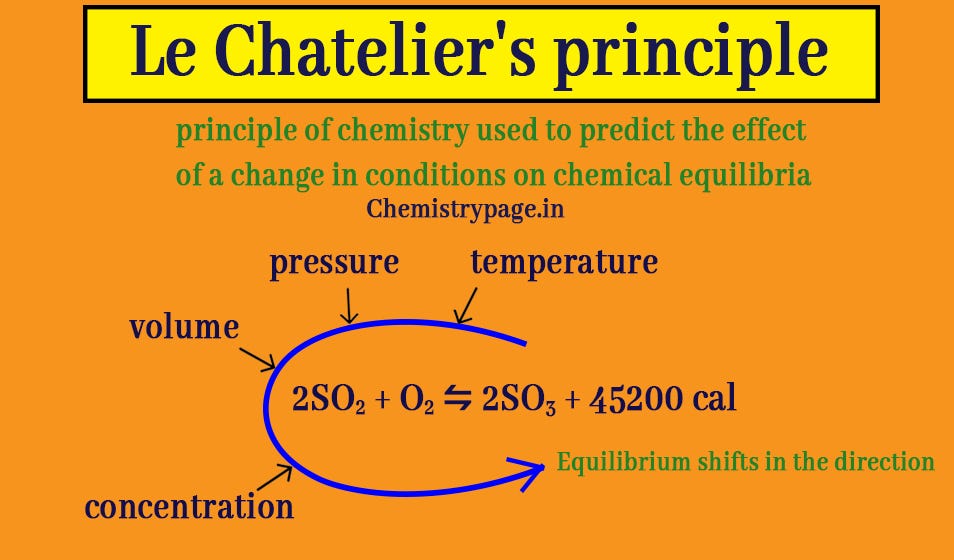
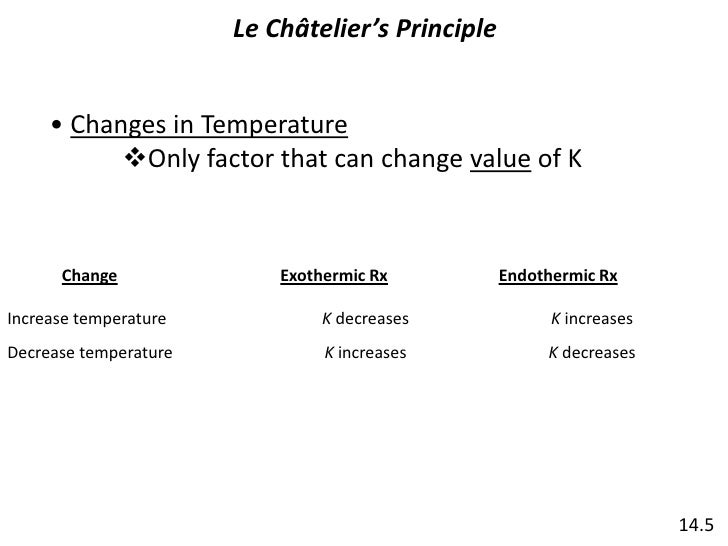
Le Chatelier's principle if the temperature is increased, the position of equilibrium moves in the endothermic direction to reduce the temperature Changing the pressureLe Chatelier and volume (pressure) Changing the volume of the container with a reaction mixture is essentially only possible for a reaction involving gases First, let's look at Le Chatelier's principle If we mechanically decrease the volume of a container of gases the pressure inside the container will increaseLeChatelier's Principle Effect of change in temperature Changes in the concentration of reactant and products affect only the position of equilibrium whereas change in temperature not only affects the position of equilibrium but also the equilibrium constant (a) Endothermic reactions are favored by the increase in temperature



Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download
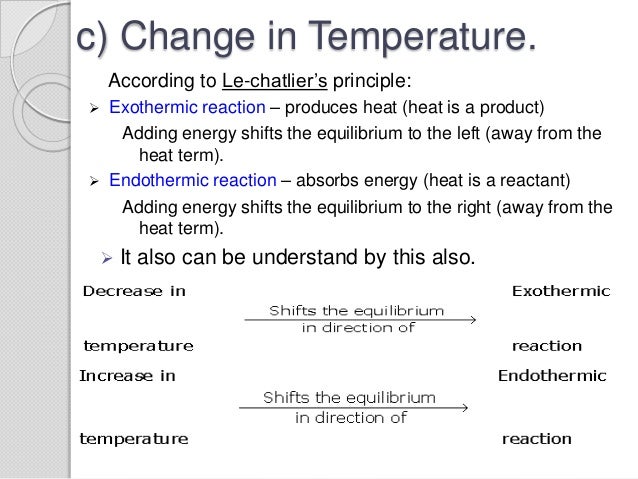


Le Chatelier S Principle 2
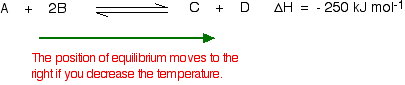
If you increase the temperature, the endothermic reaction is favored The Le Chatelier's principle states that the endothermic reaction is favored in order to minimize the effect of an increase in temperature Endothermic reactions absorb heat so the temperature must, in a way, remain constant in that systemLe Châtelier's Principle When a stress is applied to a system at Equilibrium, the system readjusts so as to relieve or offset the stress Stress is any imposed factor which upsets the balance in rates between the forward and reverse reactions In any reaction a temperature increase favours the reaction that absorbs heat ie theAccording to Le Chatelier's Principle, if you decrease the concentration of C, for example, the position of equilibrium will move to the right to increase the concentration again Note The reason for choosing an equation with "2B" will become clearer when I deal with the effect of pressure further down the page


Ppt Le Chatelier S Principle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 438


Equilibrium Dp Chemistry R Slider Ppt Video Online Download
Dec 25, · According to the law of mass action, the quantitative effects of temperature, pressure, concentration, volume and other factors on the equilibrium of a chemical reaction can be studied For the qualitative study of these factors on equilibrium, French chemist Henry Louis Le Chatelier introduced a generalized rule in 14 called le chatelier's PrincipleLe Chatelier's principle implies that the addition of heat to a reaction will favor the endothermic direction of a reaction as this reduces the amount of heat produced in the system Increasing the concentration of reactants will drive the reaction to the right, while increasing the concentration of products will drive the reaction to the leftAccording to Lechatelier's principle a change in temperature is a stress on an equilibrium system If at equilibrium the temperature of system is changed the system will no longer at remain at equilibrium To restore equilibrium, the reaction will in either forward or backward direction


Chemical Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle Youtube


Le Chatelier S Principle Chart Ganada
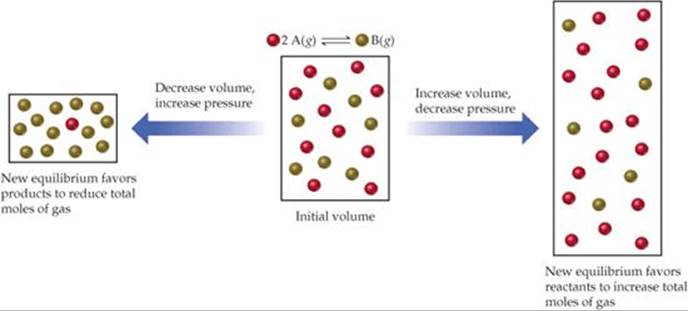
Le Chatelier's principle If a change is made to a reaction that is at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in the direction that counteracts the imposed changeBy considering the effect of changing volume on gas pressure, we can also use Le Chatelier's principle to help us predict the effect of changing volume on gas phase reactions Decreased volume leads to an increase in pressure For an ideal gas, cutting the volume in half leads to doubling the gas pressureLeChatelier's Principle, The Reaction Quotient, and the Equilibrium Constant Therefore if the reaction is exothermic as written, an increase in temperature will cause the reverse reaction to occur, decreasing the amounts of the products and increasing the amounts of reactants


Ppt Catalyst Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Ppt Applications Of Equilibrium Constants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
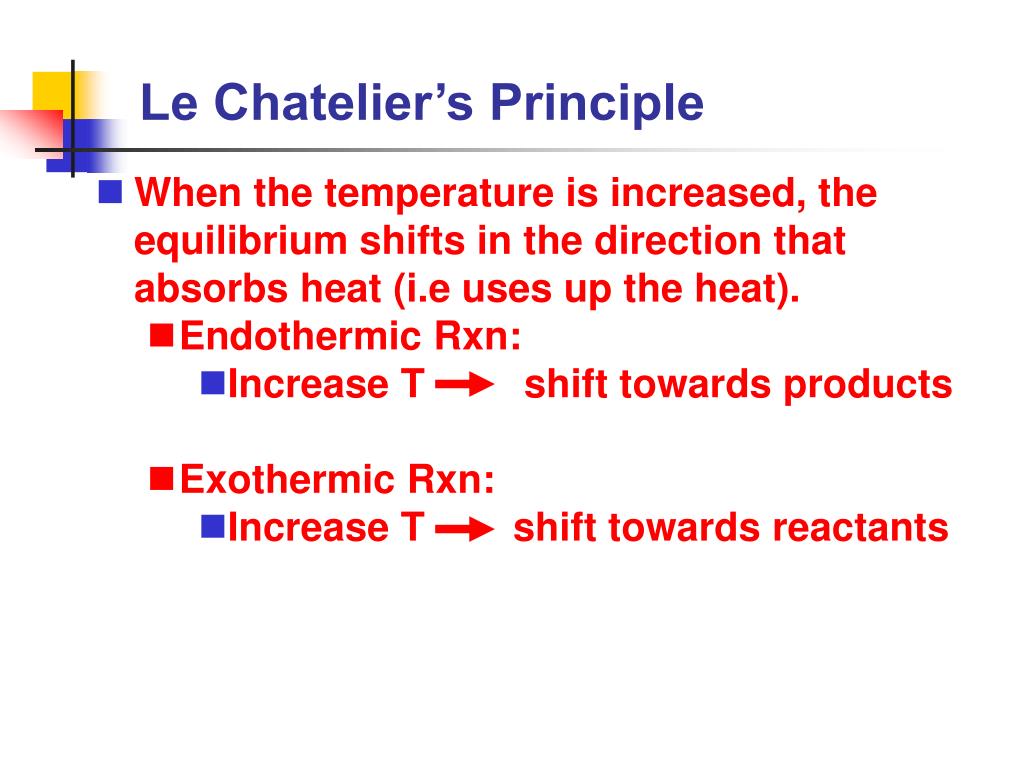
EFFECT OF CHANGE IN TEMPERATURE The effect of temperature can be understood by using le Chatelier's principle as follows 1) Increase in the temperature of the system favors the endothermic reaction The increase in temperature increases the amount of heat in the systemDr Shields discusses how to determine the direction the equilibrium will shift upon a temperature change based on the sign of the reaction enthalpy (H) GeLe Chatelier's principle is an observation about chemical equilibria of reactions It states that changes in the temperature, pressure, volume, or concentration of a system will result in predictable and opposing changes in the system in order to achieve a new equilibrium state



Le Chateliers Principle Position Of The Equilibrium Equilibrium


Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry The Central Science
Mar 04, 14 · Le Châtelier's Principle states that a change in pressure, temperature, or concentration will push the equilibrium to one side of the chemical equation So, if you manipulate the conditions to favour the product side, you increase the yield We could 1 Increase the temperature of an endothermic reaction An endothermic reaction absorbs energyIf we increase the temperature of the system, the equilibrium position will shift to the left according to Le Chatelier's Principle in order to minimise the effect of the change by consuming some of this energy This means that the concentration of the solution will decrease and the amount of undissolved solute will increaseAn increase in volume will result in a decrease in pressure at constant temperature As a result, the equilibrium will shift toward the side with the greater total moles of gas, according to Le Chatelier's Principle This will result in less AX 5 being produced The K eq tells us that the reaction favors the products because it is greater than



Reversible Reactions Equilibrium And Le Chatelier S Principle Compound Interest



Le Chatelier S Principle Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia Chemical Equilibrium Branches Of Thermodynamics
Apr 02, · By LeChatelier's principle for an exothermic reaction at equilibrium lowering of temperature will favour the forward reaction And for an endothermic reaction, an increase in temperature will favour the forward reaction Effect of the Catalyst on the Chemical EquilibriumDescribe how to use Le Chatelier's principle to predict the possible ways a chemical system can respond to changes what happens to the equilibrium when the temperature increases or decreases what happens to the equilibrium when the concentration of the reactants increasesLe chatelier's principle is a memory trick and nothing more than a memory trick UNDERSTANDING HOW TO USE IT DOES NOT MEAN THAT YOU UNDERSTAND THE CHEMISTRY BEHIND IT!!



Solved Use The Le Chatelier S Principle Interactive To An Chegg Com


Le Chatelier S Principle And More Ppt Download
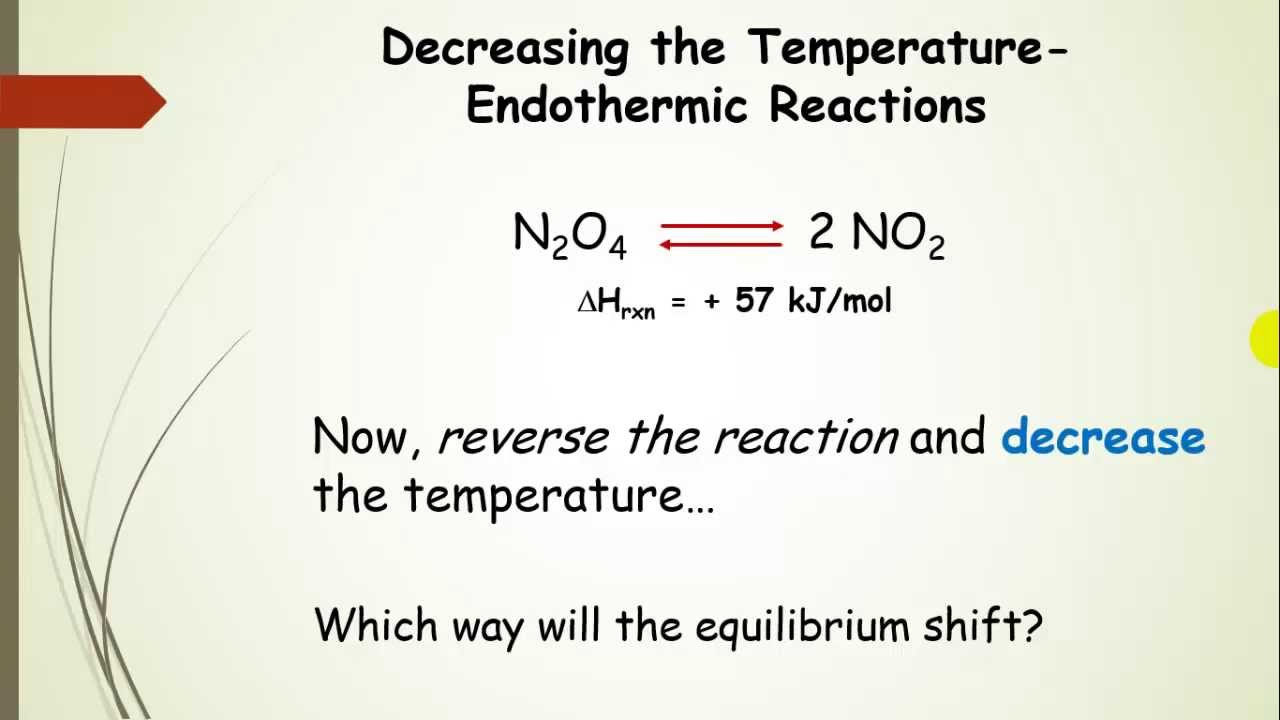
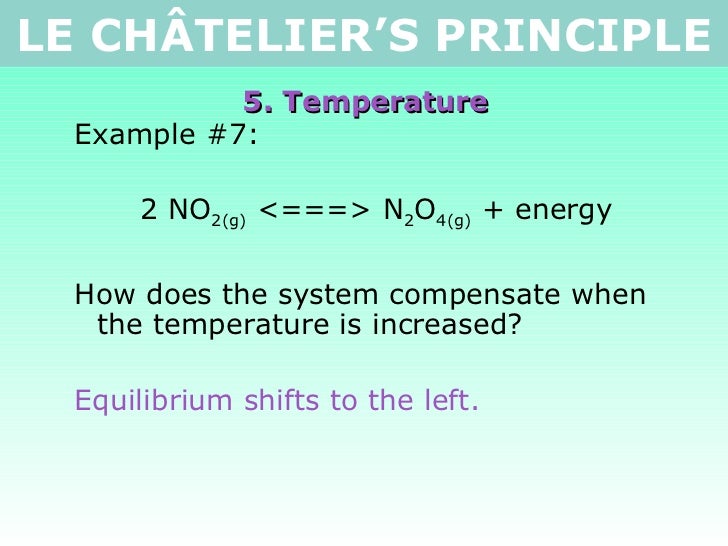
Nov 16, · Le Chatelier's principle as related to temperature changes can be illustrated easily be the reaction in which dinitrogen tetroxide is in equilibrium with nitrogen dioxide N 2O 4(g) heat ⇌ 2NO 2(g) Dinitrogen tetroxide (N 2O 4) is colorless, whileA worked example using Le Chatelier's principle to predict how concentrations will shift for different perturbations Example includes changing reaction vessel volume, changing amount of solid product, adding inert gas, and adding a catalystBy applying Le Châtelier's principle to this endothermic reaction and treating heat as a reactant, we deduce that an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium in the direction of more NO The equilibrium constant K p for formation of 1 mol of NO from its elements at 300 K is only about 1 × 10 –15 ( FIGURE 1515 )



The Position Of Equilibrium Topic 7 2 Equilibrium


Pressure Cooker Reduces Cooking Time What Is The Science Behind It By Chemistry Page Medium
The Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change of conditions, reactions occur in the system that tend to counteract the imposed change In other words, the system tends to react in a way that restores the equilibrium When the imposed stress is an increase or aDec 01, 09 · On violations of Le Chatelier's principle for a temperature change in small systems observed for short times Pouria Dasmeh, 1 Debra J Searles, 2, a 兲If we regard heat as a "reactant" or "product" in an endothermic or exothermic reaction respectively, we can use the Le Chatelier principle to predict the direction in which an increase or decrease in temperature will shift the equilibrium state Thus for the oxidation of nitrogen, an endothermic process, we can write heat N2 O2 ⇌ 2NO



Le Chatelier S Principle Chart Ganada


What Is The Le Chatelier S Principle Write The Effect Of Change In Pressure Temperature And Concentration On Equilibrium Quora
In accordance with Le Chatelier's principle, the equilibrium constant changes to minimize the change in temperature For endothermic reactions, an increase in temperature can be minimized by utilizing some of the heat to convert reactants to products, shifting the equilibrium to the right side of the reaction and increasing the value of KLe Chatelier's Principle In 14 the French chemist and engineer HenryLouis Le Chatelier proposed one of the central concepts of chemical equilibria Le Chatelier's principle can be stated as follows A change in one of the variables that describe a system at equilibrium produces a shift in the position of the equilibrium that counteracts theLe Chatelier's principle This section is an extension of the chemical equilibrium page You should be comfortable doing basic equilibrium calculations in order to understand this material The response of an equilibrium to change increase or decrease the temperature ?



03 35 Consider The Reaction Equilibrium 2 So2 G 3 2 Soz G Ah



Chemistry Not Mystery Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Change
Le Chatelier's principle higher tier The Haber Process is an exothermic reaction in the forward direction so using a low temperature would increase the yield of ammonia However this wouldLe Châtelier's Principle Temperature Increasing temperature favors the production of brown NO2in the boiling water on the left The ice cold container on the right contains more molecules of colorless N2O4, so its color is lighter DinitrogenBy Le Chatelier's principle, the system will act to consume some of the products to reduce the rate of collision and also the reverse reaction rate Concentration of reactants will increase which increases the rate of forward reaction



Worksheet Le Chatelier S Principle Name



Factors That Affect Chemical Equilibrium Boundless Chemistry


Le Chatelier S Principle Qs Study


Le Chatelier S Principle



Hsc Chemistry Le Chatelier Principle And Equilibrium Guide



Shifting Equilibrium The Effect Of Pressure Temperature And



15 Le Chatelier S Principle And Factors Affecting Equilibrium Chemical Equilibrium Chemical Reactions



Le Chatelier S Principle Chemical Equilibrium Siyavula



Le Chatelier S Principle



Le Chatelier S Principle And More Ppt Download


Factor Effecting Chemical Equilibrium Fun Science



Solved Le Chatelier S Principle 2 Parts Hydrogen Gas Ca Chegg Com



Le Chatelier S Principle Analytical Chemistry Video Clutch Prep



Le Chatelier S Principle


Le Chatelier S Principle



Equilibrium Constants Lecture 8 The Equilibrium Constant Consider


Le Chatelier S Principle Chart Ganada



What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry



Question Video Main Disadvantage Of Increased Temperature In The Haber Process Nagwa


Le Chatelier S Principle Studocu


Tang 02 Le Chatelier S Principle 2


Le Chatelier S Principle


Le Chatelier S Principle


What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry Socratic



Solved Gbdin D Use Le Chatelier S Principle To Describe Chegg Com



Le Chatelier S Principle Applications Adichemistry



Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download



Equilibrium And Le Chatelier Principle Chemical Equilibrium Operates



1 6 Chemical Equilibria And Le Chatelier S Principle Equilibrium As Secondary Science 4 All



Explaining Le Chatelier S Principle Lechateliers



Pdf On Violations Of Le Chatelier S Principle For A Temperature Change In Small Systems Observed For Short Times



Le Chatelier S Principle Studypug



Chapter 17 Rates Of Reaction Equilibrium Collision Theory


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts



Solved Based On Le Chatelier S Principle Increasing Pres Chegg Com


Chemistry Equilibrium Le Chateliers Principle Temperature And Catalysts


Le Chatelier S Principle Video Khan Academy



Le Chatelier S Principle Equilibrium Shifts Temperature Pressure Concentration Youtube


Le Chatelier S Principle Davidcalvin


Solved Volume Temperature And Le Chatelier S Principle Chegg Com



Solved Le Chatelier S Principle States That When Stress I Chegg Com



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Changes In Pressure Sl Youtube



Answered 10 1 Please Choose The Corect Bartleby



Learning Chemistry Easily Le Chatelier S Principle Effect Of Changing Temperature



Explaining Le Chatelier S Principle Lechateliers



Le Chatelier S Principle Ck 12 Foundation



Chemical Equilibrium And Le Chatelier S Principle


Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download



Question Video Applying Le Chatelier S Principle To Hydrogen Iodide Formation Nagwa
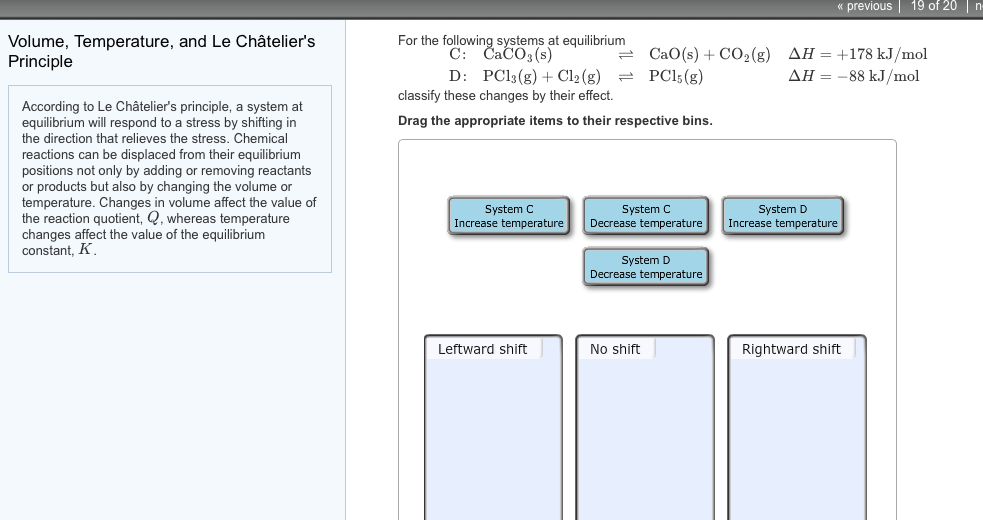


Solved Volume Temperature And Le Chatelier S Principle Chegg Com



Le Chatelier S Principle Ppt Download



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Temperature Sl Youtube


What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry


Chem 2 Chemical Equilibrium X Le Chatelier S Principle And Tempera



Equilibrium Tier 4 Apply Lechatelier S Principle To Predict The Qualitative Effects Of Changes Of Temperature Pressure And Concentration On The Position Ppt Download



7 1 Le Chatelier S Principle Changes In Temperature Sl Youtube



Le Chatelier S Principle Pv Changes On Gaseous Sytems Pt 9 Youtube



Law Of Chemical Equilibrium Le Chatelier S Principle



Le Chatelier Chemical Equilibrium Chemical Reactions



Chem 2 Chemical Equilibrium X Le Chatelier S Principle And Tempera



Chemistry The Central Science Chapter 15 Section 6
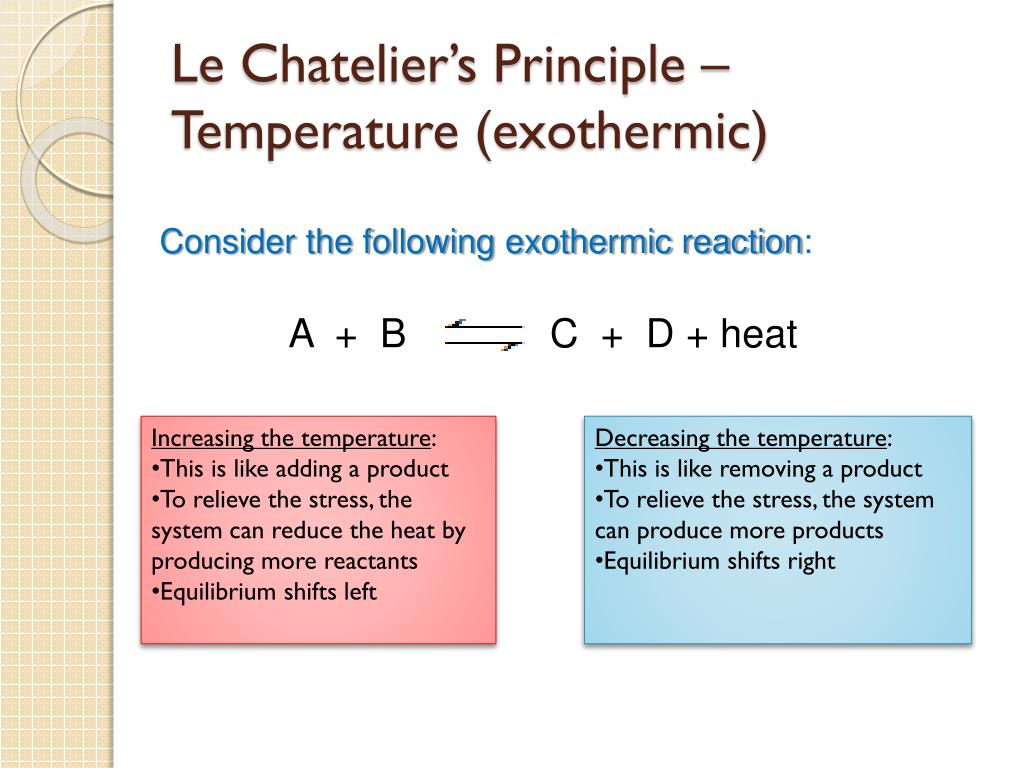


Ppt Equilibrium Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Lechatelier S Principle Equilibrium Lechatelier S Principle Co 2 Cao Caco 3 Chicken Breath Food Egg Shell I Wish I Had Sweat Glands As Temperature Ppt Download



On The Basis Of Le Chatelier Principle Explain How Temperature And



Ppt Le Chatelier S Principle Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Shifting Equilibria Le Chatelier S Principle Chemistry For Majors
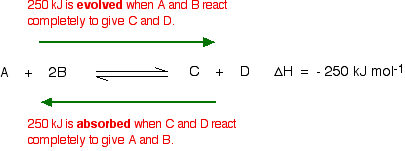


Le Chatelier S Principle



Qualitative Changes In Equilibrium Systems Ppt Download



According To Le Chteliers Principle When A Chemical



What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry Socratic



Le Chatelier S Principle
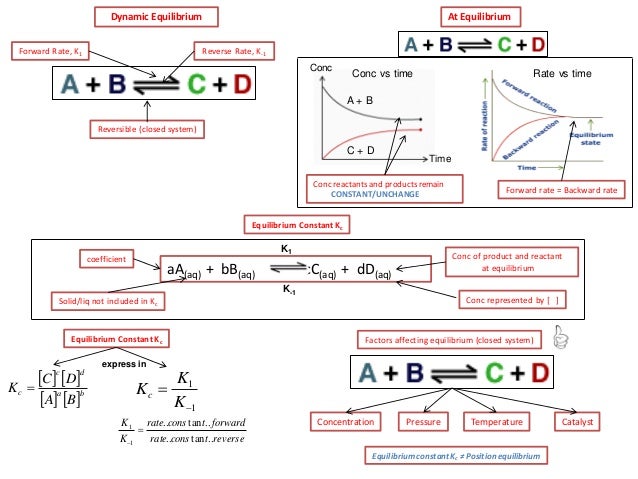


Ib Chemistry On Le Chatelier S Principle Haber And Contact Process


Le Chatelier S Principle Jee Mains
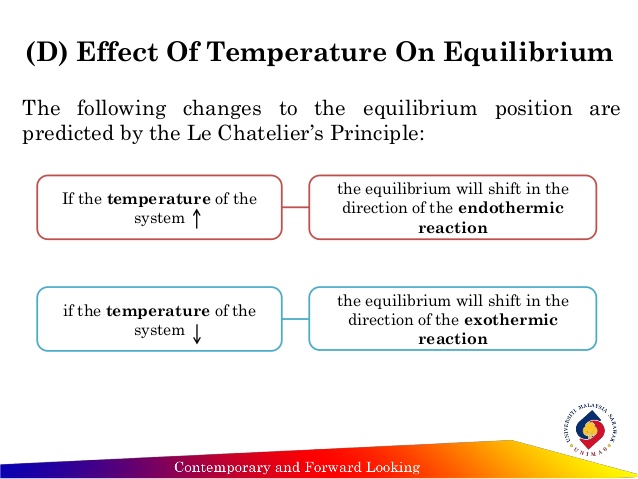


Question Cc8dd Socratic



1 6 Chemical Equilibria And Le Chatelier S Principle Equilibrium As Secondary Science 4 All



Aucun commentaire:
Publier un commentaire